Cybersecurity, the Digital Battlefield
Description, outlook and screening of the main players
Cybersecurity is one of the most interesting sectors on the stock market. The growing threat of cyber-attacks and increasing digitalization make it a buoyant market. The applications are both civil and military, as the recent conflict in Ukraine clearly illustrated. But the market is also interesting because it is in constant motion, both financially and technologically.
In this article, we will describe the world of cybersecurity. We will identify its prospects and then analyze 36 interesting players. For each, we will use our rating system to give a note in each of the following categories: growth, quality, valuation and shareholder. This will allow to identify the best investments depending on your investment style.
Sector analyses require a lot of work. If you like them, here are 3 others available: cosmetics, video games and electric vehicles. If you are interested in the cybersecurity sector here is a deep dive of Palo Alto Networks.
And without further ado, let's start our exploration!
The different types of cybersecurity and threats
Cybersecurity is not a homogeneous sector. It is multifaceted. Among the different types of segmentation, we will highlight 9:
Network security. Network security is safeguarding computer networks from various types of cyber attacks. There are different tools: firewalls, security information and event management (SIEM) tools, virtual private networks (VPNs), network segmentation, sandboxing, and intrusion prevention systems.
Information security. Information security focuses on keeping digital information safe. Some measures, including digital signatures, encryption, access control, security awareness training, and data backup and recovery, are highly effective in mitigating potential security breaches and other threats.
Application security. Application security protects mobile applications, web applications, and other software programs from cyber intrusions.
Cloud security. Cloud security refers to protecting sensitive data in the cloud environment. This concept tries to mitigate risks related to storage and system security in the cloud.
Endpoint security. Endpoint security is a concept that responds to cyber threats against individual devices such as mobile devices, servers, desktops, and laptops. Businesses or organizations enhance the security posture by implementing security measures, including Endpoint Protection Platforms (antivirus, anti-malware), Mobile Device Management (MDM) for mobile devices, and Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR).
Mobile security. Mobile security concentrates on protecting mobile devices and preventing mobile threats.
IoT security. IoT is often a weak point in a network. IoT security aims to protect IoT devices. Implementing basic measures such as a strong password policy, regular updates, and changing default settings can ensure IoT security.
Critical infrastructure security. It is the precautions to ensure essential assets that are vital and directly affecting daily life. After identifying the inventory of critical assets, implementing some measures, such as access management, continuous monitoring, improving resilience and recovery plan, managing supply chain, and network segmentation, can enhance critical infrastructure security.
Zero trust security. The Zero Trust model never trusts by default and always requires verification before granting access to sensitive data.
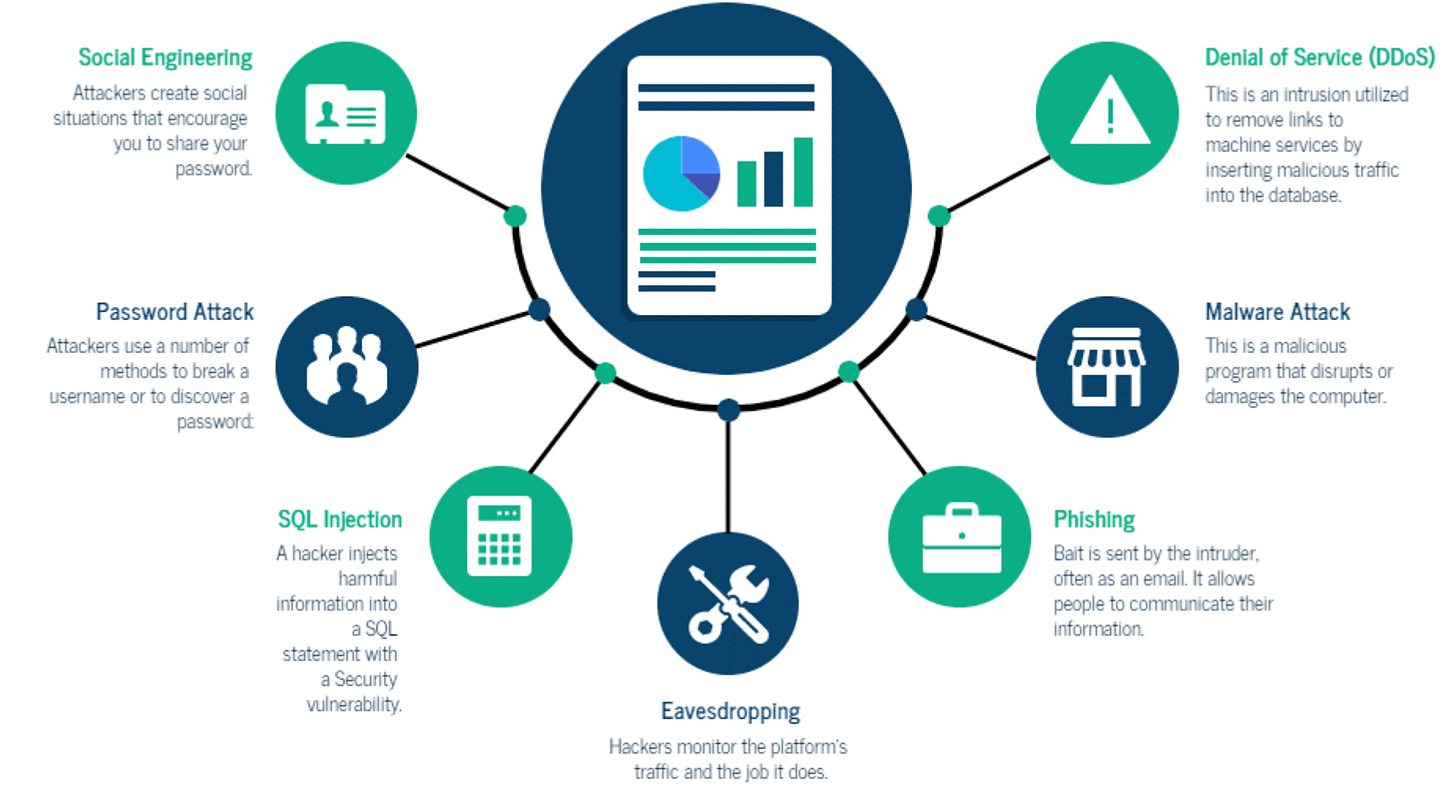
Threats can take many forms as we can see on this infographic. From social engineering to phishing.
However, a recurring element appears: human. According to a study by IBM, human error is the main cause in 95% of cyber security breaches. This leads to a first conclusion: the best cybersecurity investment is user training!
The stakes of cybersecurity
The first stake, and maybe the most understable, is the cost of cybersecurity. The global cost of cybercrime is expected to surge in the next four years, rising from $9.22 trillion in 2024 to $13.82 trillion by 2028.
The source of the costs are: damage and destruction of data, stolen money, lost productivity, theft of intellectual property, theft of personal and financial data, embezzlement, fraud, post-attack disruption to the normal course of business, forensic investigation, restoration and deletion of hacked data and systems, and reputational harm.
Beyond cost, cybersecurity has become part of the arsenal in geopolitical conflicts, both in “peaceful time” for spying, business intelligence, technological theft and in war time.
As an example, according to a report from the Cyber Peace Institute, between January 2022 and September 2023, the conflict in Ukraine generated:
574 cyber attacks targeting Ukraine
306 cyber attacks targeting Russia
1,896 cyber attacks targeting third countries (mainly Poland, Lithuania, Germany and the USA)
The targets were various. Among them, we can find public administrations, banks and companies/organizations from different sectors (transportation, administration or media).
The goals of these cyberattacks were:
Disruption
Data theft
Disinformation
Destruction
As more and more critical systems go online, it is easy to see how important cybersecurity is to modern warfare.
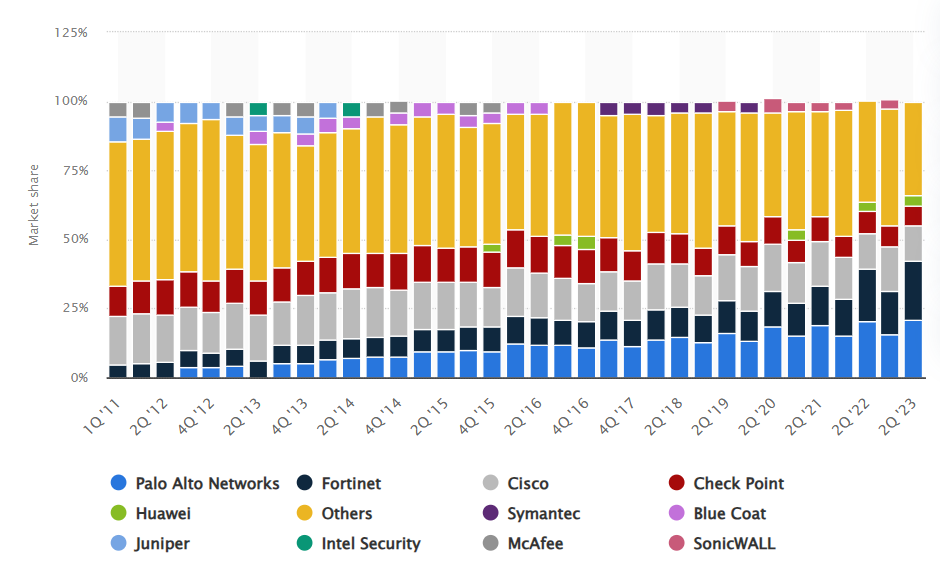
Marketshare and consolidation
The security appliance vendor market is slowly consolidating.
But it remains highly fragmented. This consolidation will be accentuated by the customers pursuing a vendor consolidation strategy to limit the number of software in their IT architectures and therefore reduce cost.
This consolidation will give some advantages to the company with huge financial capabilities and strong execution, basically the leaders.
Market outlook and CAGR
Before looking at the 36 interesting cybersecurity stock (including their score in the 5 categories: growth, quality, valuation, shareholder, market), let’s take a look at the estimated market size by 2030 to identify the long-term growth potential.
Keep reading with a 7-day free trial
Subscribe to Quality Stocks to keep reading this post and get 7 days of free access to the full post archives.